Capital is a generic word that is usually associated with financial and other resources that individuals and businesses collect and raise in order to improve their economical power and develop an edge in the market. It can come in many forms, as it consists of financial resources (including cash, stocks, and shares), human resources, natural resources, and other forms that produce income to investors.
Uses for capital
Capital can produce value in multiple forms: One of which is providing liquidity.
Liquidity allows businesses to buy materials, machinery, and pay workers in order to run and maintain the business- ultimately creating revenue and income that goes back to increase the capital, thus increasing operations. And the loop goes on.
Also, capital improves the balance sheet by paying off loans and other liabilities, and increasing owner's equity. This will directly improve the economic health of the business. Thus it may be able to make further activities and acquisitions that previously were too large or risky.
Where to collect capital from?
Capital is the economic backbone that allows businesses to operate, and thus it is necessary to have sufficient capital when starting or running a startup or a business. While one can invest in his/her own business from their savings- often this is not the case as saving and personal finance is rarely sufficient to sustain a business. This is why founders usually go hunting for methods to raise capital before they hit the ground.
There are multiple methods to collect capital, but to keep it simple we will look into the two main overall methods used: Equity and Debt.
-
Equity capital
When business owners want to raise capital, the often issue investible partitions in the business so that investors can become shareholders through shares that translates into ownership in the business. The benefit of this method is raising capital without commitment of repaying it back (like in Debt capital), but the downside is giving out ownership of the business. -
Debt capital
Debt capital is gained through loans and similar financial activities that need to be re-payed over time. The benefit of this method is raising capital quickly without selling parts of the business (like in Equity capital), but the downside is having to pay the loan back regardless the health of the business- i.e. loan has to be paid back regardless of the business becoming profitable or suffering losses.
Capital is not only "money"
Capital is defined as an economic value that can be translated into money. Still, it is much more than that. Money is indeed part of capital in a passive sense, while capital itself is a larger term that includes forms of economic value that are used by an individual or business to bring wealth. This may include stocks, land, cash, and other forms of economic value.
What are the different forms of capital?
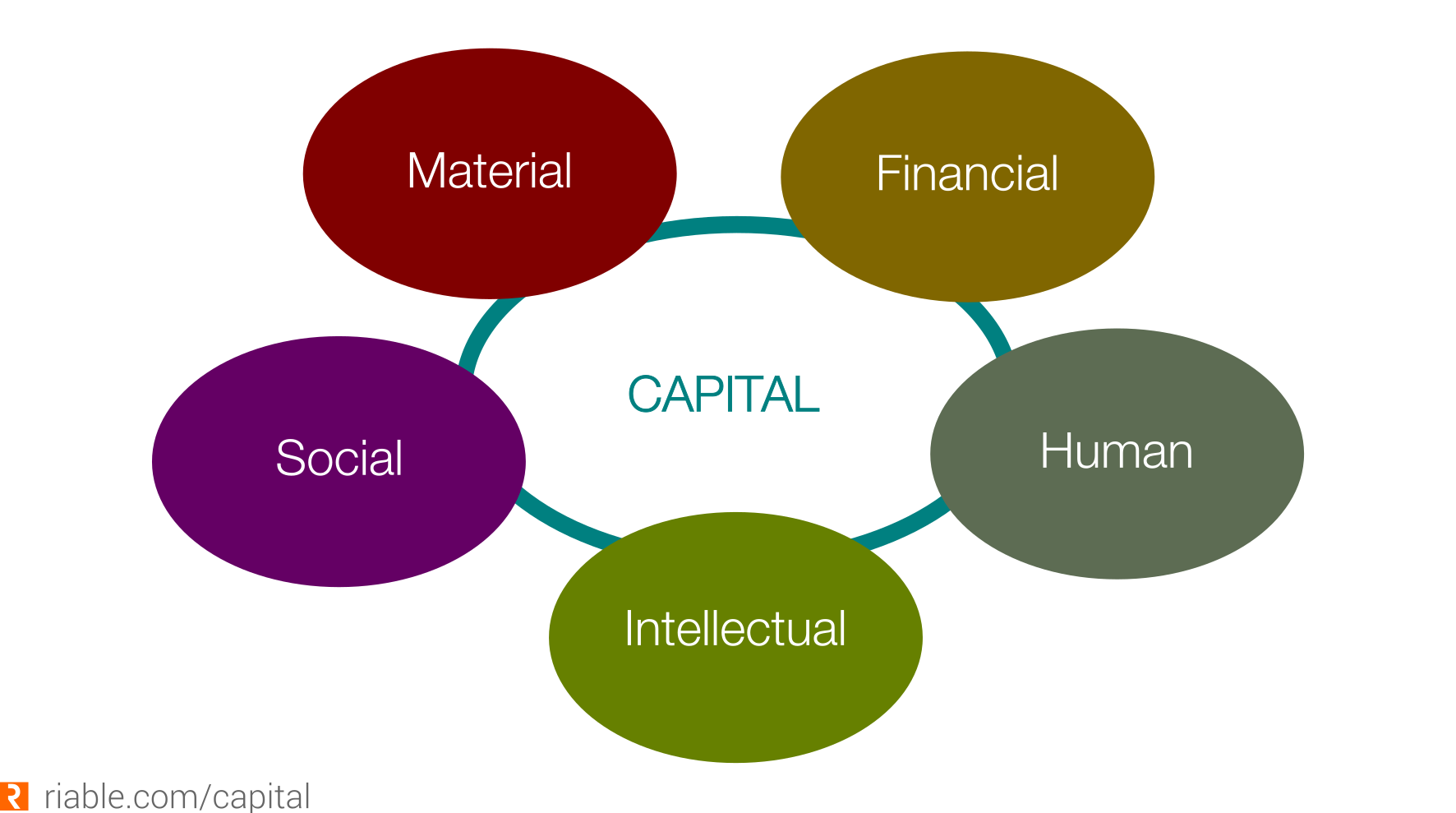
- Financial capital
Financial capital (referred to as equity) is the most common form of capital and when you hear the word 'capital' alone this is usually what it refers to. This form of capital consists of monetary resources used by entrepreneurs and businesses to buy tools and equipment to help them create value in the form of products and services. This form can include savings, loans, shares and stocks- among others. - Human capital
Human capital refers to value that a business possesses in terms of human skills, personality, and creativity that a certain person or group of persons bring to the business. The main characteristic that makes this form of capital different than Financial capital is that Financial capital is tangible whereas Human capital is intangible. Nevertheless, human capital form an essential measure in valuating companies. - Intellectual capital
Intellectual capital is considered a sub-part of the Human capital, but it is unique in the sense that it focuses on the intellectual skills and capabilities a company possesses, such as Intellectual Property (IP). - Social capital
Social capital is another form of intangible capital that measures the degree to which an person or a group of persons are connected. If it is in good standing with a multitude of connections locally and abroad, it is said to have a good Social capital. - Material capital
Includes physical goods, equipment, raw materials and other physical items. This is considered as capital as long as it can be sold and valued in money.
Is capital fixed or dynamic?
Capital can be either fixed or dynamic (called Working capital). Fixed capital is long-term and used to back the company over the long run, while working capital is more operational and can be used to bring immediate gains. The following table classifies each:
Fixed capital: Fixed capital is money that remains permanently in the business and help it make a profit and buy assets.
Working capital: Working capital is used to run the business operations.
| Fixed capital | Working capital | |
| Meaning | Investment by business to bring long-term benefits | Daily or periodic requirement invested into a business |
| Nature | Used to purchase non-current assets that remain for the long-term | Used to purchase current assets that remain for the short-term |
| Conversion | Not liquid, and cannot be transformed into cash immediately | Usually liquid, and can be transformed into cash quickly |
| Examples | Buying a land, building, and heavy equipment for the business | Inventory and short-term loans acquired by a business to run its operations |
The nature of capital
- Capital is passive
In essence, capital forms the economic backbone of the business and the infrastructure on top of which a business can operate and thrive. Given this, capital itself is passive and is only beneficial once it gets working for the benefit of owners via activities.
- Capital is a Man-made
Linked to the previous point, capital is made by human based activities. In the same sense, human efforts can increase capital or decrease it.
- Capital is easy to move
Capital is mobile- it can be allocated and re-allocated easier than other economic forms such as land and labor that are difficult to relocate.
- Capital is subject to deprecation
Capital can deprecate with time and human activities. It can replenish and be reproduced.